Decoding a Black Hole: From Scrambling to Information Loss¶
Hayden-Preskill Thought Experiment + Yoshida-Kitaev Protocol¶
1. Information Loss Puzzle¶
Fundamental Conflict Between Quantum Mechanics and General Relativity¶
Quantum mechanics states: Information is never lost
$$|\psi(t)\rangle = e^{-i\hat{H}t/\hbar}|\psi(0)\rangle$$
Unitary evolution preserves information - any quantum process is in principle reversible.
General relativity suggests: Information falling into a black hole is lost forever
- Black holes emit thermal Hawking radiation
- After complete evaporation of the black hole, all information should vanish
- This would violate unitarity of quantum mechanics
2. Hayden-Preskill Thought Experiment (2007)¶
Basic Setup¶
Protagonists:
- Alice: owns a quantum state |ψ⟩ that she wants to send into the black hole
- Bob: owns a quantum memory M that is maximally entangled with the black hole
Scenario:
- The black hole has already radiated ~50% of its content (reached Page time)
- At this moment, the black hole is maximally entangled with the previous Hawking radiation
- Bob collects this radiation and maintains it in his quantum memory M
Key Finding:
After Page time, information begins to leak out rapidly from the black hole through Hawking radiation!
Two Types of Black Holes¶
A) Evaporating Black Hole¶
- Starts with a large amount of mass
- Gradually emits Hawking radiation
- After radiating ~50% of content, reaches Page time
- Continues evaporating until complete disappearance
B) Eternal AdS Black Hole (eternal black hole in Anti-de Sitter space)¶
- Maintains constant size
- In thermal equilibrium with its radiation
- Described by the thermofield double state
- This model is more suitable for quantum experiments
3. Simulation of the black hole information paradox¶
Circuit structure:¶
- q0: falling qubit carrying unknown information
- q1-q4: black hole that entangle the information
- q5: external reference qubit that remains outside the black hole
- q6: used for collecting qubits emitted as Hawking radiation
- q7: used for verifying quantum correlations
- After scrambling, we gradually "emit" qubits as Hawking radiation
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit, QuantumRegister, ClassicalRegister
from qiskit.quantum_info import DensityMatrix, partial_trace, entropy
from qiskit_aer import AerSimulator
from qiskit import transpile
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scrambling_circuit import ScramblingCircuit
m_rnd_value = 80
scramble_depth = 4
%matplotlib inline
np.random.seed(m_rnd_value)
4. Circuits¶
def hp_circuit1():
qr = QuantumRegister(8, 'q')
cr = ClassicalRegister(2, 'c')
qc = QuantumCircuit(qr, cr)
qc.h(qr[5])
qc.h(qr[7])
qc.cx(qr[5], qr[0])
qc.cz(qr[0], qr[5])
qc.barrier(label='Bell A↔R')
qc.h(qr[0])
qc.barrier(label='BH init')
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[1])
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[2])
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[3])
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[4])
qc.barrier(label='q0→BH')
# === Scrambling - systematic CNOT cascades ===
for source in range(5):
for target in range(5):
if source != target:
qc.cx(qr[source], qr[target])
for i in range(5):
qc.rx(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.ry(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.rz(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.barrier(label='Scramble')
qc.cx(qr[2], qr[6])
qc.cx(qr[3], qr[6])
qc.cx(qr[4], qr[6])
qc.h(qr[6])
qc.cswap(qr[7],qr[6],qr[5])
qc.h(qr[7])
qc.barrier(label='Radiation→q6')
return qc, qr, cr
def hp_circuit2(scramble_depth=scramble_depth):
"""
Hayden-Preskill circuit.
"""
qr = QuantumRegister(8, 'q')
cr = ClassicalRegister(2, 'c')
qc = QuantumCircuit(qr, cr)
# ========== 1. Bell pair: q0 (falling) ↔ q5 (reference) ==========
# |Φ+⟩ = (|00⟩ + |11⟩)/√2
# q5 stays OUTSIDE as reference
qc.h(qr[5])
qc.h(qr[7])
qc.cx(qr[5], qr[0])
qc.cz(qr[0], qr[5])
qc.barrier(label='Bell q0↔q5')
# ========== 2. Black hole (q1-q4) in initial state ==========
# We can initialize as maximally mixed state
qc.h(qr[0])
#for i in range(0, 5): # q1-q4
# qc.h(qr[i])
#for i in range(0, 5):
# qc.h(qr[i])
qc.barrier(label='BH init')
# ========== 3. q0 falls into the black hole ==========
# Interaction of falling qubit with BH qubits
for i in range(1, 5):
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[i])
qc.barrier(label='q0→BH')
# ========== 4. Scrambling inside the black hole ==========
for layer in range(scramble_depth):
# Random single-qubit rotations on BH (q0-q4)
for i in range(5):
qc.rx(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.ry(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.rz(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
# CNOT layer (forward) - only within BH
for i in range(4):
qc.cx(qr[i], qr[i+1])
# CNOT layer (backward)
for i in range(3, -1, -1):
qc.cx(qr[i+1], qr[i])
qc.barrier(label='Scramble')
# ========== 5. Hawking radiation emission to q6 ==========
# Qubits from BH (q1, q2, q3) radiate information to q6
#qc.cx(qr[1], qr[6])
qc.cx(qr[2], qr[6])
qc.cx(qr[3], qr[6])
qc.cx(qr[4], qr[6])
qc.h(qr[6])
qc.cswap(qr[7],qr[6],qr[5])
qc.h(qr[7])
qc.barrier(label='Radiation→q6')
return qc, qr, cr
5a. Visualisation circuits¶
qc, qr, cr = hp_circuit1()
qc.draw(output='mpl', fold=80, scale=0.6)
5b. Visualisation circuits¶
qc, qr, cr = hp_circuit2(scramble_depth=scramble_depth)
qc.draw(output='mpl', fold=80, scale=0.6)
6a. Analysis: Mutual Information vs Number of Emitted Qubits¶
def analyze_emission(qc, n_emitted):
"""
Modified analysis for correct qubit structure:
- q0: falling qubit (in BH)
- q1-q4: black hole
- q5: REFERENCE - Bell pair with q0
- q6: Hawking radiation
- q7: SWAP test (not used here)
Emission: we gradually "radiate" qubits from BH (q0, q1, q2, q3, q4)
"""
sim = AerSimulator(method='statevector')
qc_copy = qc.copy()
qc_copy.save_statevector()
result = sim.run(transpile(qc_copy, sim)).result()
rho = DensityMatrix(result.get_statevector())
all_q = set(range(8))
ref = [5]
# Radiation = first n_emitted qubits from BH (q0, q1, ...)
rad = list(range(n_emitted)) if n_emitted > 0 else []
# BH remainder = from n_emitted to q4 (total 5 BH qubits: q0-q4)
bh = list(range(n_emitted, 5))
def S(sub):
if not sub:
return 0.0
return entropy(partial_trace(rho, list(all_q - set(sub))), base=2)
def MI(A, B):
if not A or not B:
return 0.0
return S(A) + S(B) - S(list(set(A) | set(B)))
return {
'n_emitted': n_emitted,
'fraction': n_emitted / 5, # 5 qubits in BH
'I(R:Rad)': MI(ref, rad),
'I(R:BH)': MI(ref, bh),
'S(R)': S(ref),
'S(Rad)': S(rad),
'S(BH)': S(bh),
}
qc_full, qr, cr = hp_circuit1()
# Analysis for different numbers of emitted qubits
results = []
for n in range(7):
res = analyze_emission(qc_full, n)
results.append(res)
print(f"S(Reference) = {results[0]['S(R)']:.4f} bits\n")
print("Emitted | Fraction | I(R:Rad) | I(R:BH) | S(Rad) | S(BH)")
print("-" * 70)
for res in results:
marker = " ← Page time" if res['n_emitted'] == 3 else ""
print(f" {res['n_emitted']} | {res['fraction']:.2f} | {res['I(R:Rad)']:.4f} | {res['I(R:BH)']:.4f} | {res['S(Rad)']:.4f} | {res['S(BH)']:.4f}{marker}")
S(Reference) = 1.0000 bits
Emitted | Fraction | I(R:Rad) | I(R:BH) | S(Rad) | S(BH)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
0 | 0.00 | 0.0000 | 1.1887 | 0.0000 | 2.0000
1 | 0.20 | 0.4512 | 0.4512 | 1.0000 | 1.0000
2 | 0.40 | 0.4512 | 0.4512 | 1.0000 | 1.0000
3 | 0.60 | 0.7736 | 0.1917 | 1.9908 | 0.9994 ← Page time
4 | 0.80 | 0.7754 | 0.1899 | 1.9957 | 0.9987
5 | 1.00 | 1.1887 | 0.0000 | 2.0000 | 0.0000
6 | 1.20 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.8113 | 0.0000
7a. Visualisation: Page curve¶
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5))
fig.suptitle('Hayden-Preskill Protocol: Information Escaping', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
n_emit = [r['n_emitted'] for r in results]
fracs = [r['fraction'] for r in results]
I_rad = [r['I(R:Rad)'] for r in results]
I_bh = [r['I(R:BH)'] for r in results]
S_rad = [r['S(Rad)'] for r in results]
# 1. Mutual Information
ax1 = axes[0]
ax1.plot(n_emit, I_rad, 'b-o', lw=2, ms=10, label='I(Reference : Radiation)')
ax1.plot(n_emit, I_bh, 'r--s', lw=2, ms=8, label='I(Reference : BH)')
ax1.axvline(x=3, color='green', linestyle=':', lw=2, alpha=0.7, label='Page time')
ax1.set_xlabel('Number of emitted qubits', fontsize=11)
ax1.set_ylabel('Mutual Information [bits]', fontsize=11)
ax1.set_title('Where does information escape to?')
ax1.legend(loc='center right')
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax1.set_xticks(n_emit)
# 2. Page curve - S(Radiation)
ax2 = axes[1]
ax2.plot(n_emit, S_rad, 'm-^', lw=2, ms=10, label='S(Radiation)')
# Theoretical Page curve
page_theory = [min(k, 6-k) for k in range(7)]
ax2.plot(n_emit, page_theory, 'g--', lw=2, alpha=0.5, label='Page curve (ideal)')
ax2.axvline(x=3, color='green', linestyle=':', lw=2, alpha=0.7)
ax2.set_xlabel('Number of emitted qubits', fontsize=11)
ax2.set_ylabel('Entropy [bits]', fontsize=11)
ax2.set_title('Page Curve')
ax2.legend()
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax2.set_xticks(n_emit)
# 3. Information fraction in radiation
ax3 = axes[2]
total = [r + b for r, b in zip(I_rad, I_bh)]
ratio = [r/t*100 if t > 0.01 else 0 for r, t in zip(I_rad, total)]
colors = ['#2196F3' if r < 50 else '#4CAF50' for r in ratio]
ax3.bar(n_emit, ratio, color=colors, edgecolor='black', alpha=0.8)
ax3.axhline(y=50, color='red', linestyle='--', lw=2, alpha=0.7, label='50% threshold')
ax3.axvline(x=3, color='green', linestyle=':', lw=2, alpha=0.7, label='Page time')
ax3.set_xlabel('Number of emitted qubits', fontsize=11)
ax3.set_ylabel('Information fraction in radiation [%]', fontsize=11)
ax3.set_title('Decodability from radiation')
ax3.set_ylim(0, 110)
ax3.legend()
ax3.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax3.set_xticks(n_emit)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
8a. Statistics across different scrambling realizations¶
def run_multiple_realizations(n_realizations=5, scramble_depth=scramble_depth, m_rnd_value=m_rnd_value):
"""Averages over different random scrambling unitaries."""
all_I_rad = []
all_I_bh = []
for seed in range(n_realizations):
np.random.seed(seed * 17 + m_rnd_value)
qc, _, _ = hp_circuit1()
I_rad_run = []
I_bh_run = []
for n in range(7):
res = analyze_emission(qc, n)
I_rad_run.append(res['I(R:Rad)'])
I_bh_run.append(res['I(R:BH)'])
all_I_rad.append(I_rad_run)
all_I_bh.append(I_bh_run)
return {
'mean_I_rad': np.mean(all_I_rad, axis=0),
'std_I_rad': np.std(all_I_rad, axis=0),
'mean_I_bh': np.mean(all_I_bh, axis=0),
'std_I_bh': np.std(all_I_bh, axis=0),
}
stats = run_multiple_realizations(n_realizations=5)
print("Emitted | I(R:Rad) mean±std | I(R:BH) mean±std")
print("-" * 55)
for n in range(7):
marker = " ← Page" if n == 3 else ""
print(f" {n} | {stats['mean_I_rad'][n]:.3f} ± {stats['std_I_rad'][n]:.3f} | {stats['mean_I_bh'][n]:.3f} ± {stats['std_I_bh'][n]:.3f}{marker}")
Emitted | I(R:Rad) mean±std | I(R:BH) mean±std
-------------------------------------------------------
0 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 1.188 ± 0.001
1 | 0.451 ± 0.000 | 0.451 ± 0.001
2 | 0.451 ± 0.000 | 0.451 ± 0.001
3 | 0.711 ± 0.089 | 0.252 ± 0.082 ← Page
4 | 0.823 ± 0.056 | 0.169 ± 0.023
5 | 1.188 ± 0.001 | 0.000 ± 0.000
6 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | 0.000 ± 0.000
# Visualization with error bars
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
x = list(range(7))
ax.errorbar(x, stats['mean_I_rad'], yerr=stats['std_I_rad'],
fmt='o-', capsize=5, capthick=2, color='blue',
ecolor='lightblue', lw=2, ms=10, label='I(R : Radiation)')
ax.errorbar(x, stats['mean_I_bh'], yerr=stats['std_I_bh'],
fmt='s--', capsize=5, capthick=2, color='red',
ecolor='lightcoral', lw=2, ms=8, label='I(R : BH)')
ax.axvline(x=3, color='green', linestyle=':', lw=2, label='Page time')
ax.fill_between(x,
np.array(stats['mean_I_rad']) - np.array(stats['std_I_rad']),
np.array(stats['mean_I_rad']) + np.array(stats['std_I_rad']),
alpha=0.2, color='blue')
ax.set_xlabel('Number of emitted qubits', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('Mutual Information [bits]', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('Hayden-Preskill: Statistics across different scrambling realizations', fontsize=13)
ax.legend(fontsize=11)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xticks(x)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
6b. Analysis: Mutual Information vs Number of Emitted Qubits¶
qc_full, qr, cr = hp_circuit2(scramble_depth=scramble_depth)
# Analysis for different numbers of emitted qubits
results2 = []
for n in range(7):
res = analyze_emission(qc_full, n)
results2.append(res)
print(f"S(Reference) = {results2[0]['S(R)']:.4f} bits\n")
print("Emitted | Fraction | I(R:Rad) | I(R:BH) | S(Rad) | S(BH)")
print("-" * 70)
for res in results2:
marker = " ← Page time" if res['n_emitted'] == 3 else ""
print(f" {res['n_emitted']} | {res['fraction']:.2f} | {res['I(R:Rad)']:.4f} | {res['I(R:BH)']:.4f} | {res['S(Rad)']:.4f} | {res['S(BH)']:.4f}{marker}")
S(Reference) = 0.9997 bits
Emitted | Fraction | I(R:Rad) | I(R:BH) | S(Rad) | S(BH)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
0 | 0.00 | 0.0000 | 1.2028 | 0.0000 | 1.9877
1 | 0.20 | 0.0132 | 1.0825 | 0.8814 | 2.6762
2 | 0.40 | 0.1369 | 0.6589 | 1.6108 | 2.6419
3 | 0.60 | 0.3140 | 0.1305 | 2.2239 | 1.9027 ← Page time
4 | 0.80 | 0.7901 | 0.0346 | 2.3229 | 0.9779
5 | 1.00 | 1.2028 | 0.0000 | 1.9877 | 0.0000
6 | 1.20 | 0.9997 | 0.0000 | 1.7845 | 0.0000
7b. Visualisation: Page curve¶
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5))
fig.suptitle('Hayden-Preskill Protocol: Information Escaping', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
n_emit = [r['n_emitted'] for r in results2]
fracs = [r['fraction'] for r in results2]
I_rad = [r['I(R:Rad)'] for r in results2]
I_bh = [r['I(R:BH)'] for r in results2]
S_rad = [r['S(Rad)'] for r in results2]
# 1. Mutual Information
ax1 = axes[0]
ax1.plot(n_emit, I_rad, 'b-o', lw=2, ms=10, label='I(Reference : Radiation)')
ax1.plot(n_emit, I_bh, 'r--s', lw=2, ms=8, label='I(Reference : BH)')
ax1.axvline(x=3, color='green', linestyle=':', lw=2, alpha=0.7, label='Page time')
ax1.set_xlabel('Number of emitted qubits', fontsize=11)
ax1.set_ylabel('Mutual Information [bits]', fontsize=11)
ax1.set_title('Where does information escape to?')
ax1.legend(loc='center right')
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax1.set_xticks(n_emit)
# 2. Page curve - S(Radiation)
ax2 = axes[1]
ax2.plot(n_emit, S_rad, 'm-^', lw=2, ms=10, label='S(Radiation)')
# Theoretical Page curve
page_theory = [min(k, 6-k) for k in range(7)]
ax2.plot(n_emit, page_theory, 'g--', lw=2, alpha=0.5, label='Page curve (ideal)')
ax2.axvline(x=3, color='green', linestyle=':', lw=2, alpha=0.7)
ax2.set_xlabel('Number of emitted qubits', fontsize=11)
ax2.set_ylabel('Entropy [bits]', fontsize=11)
ax2.set_title('Page Curve')
ax2.legend()
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax2.set_xticks(n_emit)
# 3. Information fraction in radiation
ax3 = axes[2]
total = [r + b for r, b in zip(I_rad, I_bh)]
ratio = [r/t*100 if t > 0.01 else 0 for r, t in zip(I_rad, total)]
colors = ['#2196F3' if r < 50 else '#4CAF50' for r in ratio]
ax3.bar(n_emit, ratio, color=colors, edgecolor='black', alpha=0.8)
ax3.axhline(y=50, color='red', linestyle='--', lw=2, alpha=0.7, label='50% threshold')
ax3.axvline(x=3, color='green', linestyle=':', lw=2, alpha=0.7, label='Page time')
ax3.set_xlabel('Number of emitted qubits', fontsize=11)
ax3.set_ylabel('Information fraction in radiation [%]', fontsize=11)
ax3.set_title('Decodability from radiation')
ax3.set_ylim(0, 110)
ax3.legend()
ax3.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax3.set_xticks(n_emit)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
8b. Statistics across different scrambling realizations¶
def run_multiple_realizations2(n_realizations=5, scramble_depth=scramble_depth, m_rnd_value=m_rnd_value):
"""Averages over different random scrambling unitaries."""
all_I_rad = []
all_I_bh = []
for seed in range(n_realizations):
np.random.seed(seed * 17 + m_rnd_value)
qc, _, _ = hp_circuit2(scramble_depth)
I_rad_run = []
I_bh_run = []
for n in range(7):
res = analyze_emission(qc, n)
I_rad_run.append(res['I(R:Rad)'])
I_bh_run.append(res['I(R:BH)'])
all_I_rad.append(I_rad_run)
all_I_bh.append(I_bh_run)
return {
'mean_I_rad': np.mean(all_I_rad, axis=0),
'std_I_rad': np.std(all_I_rad, axis=0),
'mean_I_bh': np.mean(all_I_bh, axis=0),
'std_I_bh': np.std(all_I_bh, axis=0),
}
stats2 = run_multiple_realizations2(n_realizations=5)
print("Emitted | I(R:Rad) mean±std | I(R:BH) mean±std")
print("-" * 55)
for n in range(7):
marker = " ← Page" if n == 3 else ""
print(f" {n} | {stats2['mean_I_rad'][n]:.3f} ± {stats2['std_I_rad'][n]:.3f} | {stats2['mean_I_bh'][n]:.3f} ± {stats2['std_I_bh'][n]:.3f}{marker}")
Emitted | I(R:Rad) mean±std | I(R:BH) mean±std
-------------------------------------------------------
0 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 1.154 ± 0.050
1 | 0.030 ± 0.021 | 1.054 ± 0.048
2 | 0.169 ± 0.046 | 0.609 ± 0.099
3 | 0.452 ± 0.083 | 0.169 ± 0.048 ← Page
4 | 0.971 ± 0.057 | 0.052 ± 0.028
5 | 1.154 ± 0.050 | 0.000 ± 0.000
6 | 1.000 ± 0.001 | 0.000 ± 0.000
# Visualization with error bars
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
x = list(range(7))
ax.errorbar(x, stats2['mean_I_rad'], yerr=stats2['std_I_rad'],
fmt='o-', capsize=5, capthick=2, color='blue',
ecolor='lightblue', lw=2, ms=10, label='I(R : Radiation)')
ax.errorbar(x, stats2['mean_I_bh'], yerr=stats2['std_I_bh'],
fmt='s--', capsize=5, capthick=2, color='red',
ecolor='lightcoral', lw=2, ms=8, label='I(R : BH)')
ax.axvline(x=3, color='green', linestyle=':', lw=2, label='Page time')
ax.fill_between(x,
np.array(stats2['mean_I_rad']) - np.array(stats2['std_I_rad']),
np.array(stats2['mean_I_rad']) + np.array(stats2['std_I_rad']),
alpha=0.2, color='blue')
ax.set_xlabel('Number of emitted qubits', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('Mutual Information [bits]', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('Hayden-Preskill: Statistics across different scrambling realizations', fontsize=13)
ax.legend(fontsize=11)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xticks(x)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
9. Entanglement verification of both circuits¶
qc_orig, _, _ = hp_circuit1()
sim = AerSimulator(method='statevector')
qc_orig.save_statevector()
result = sim.run(transpile(qc_orig, sim)).result()
rho = DensityMatrix(result.get_statevector())
S_q7_orig = entropy(partial_trace(rho, [0,1,2,3,4,5,6]), base=2)
print(f"\nCircuit1:")
print(f" S(q7) = {S_q7_orig:.4f} bits")
print(f" q7 {'IS' if S_q7_orig > 0.1 else 'IS NOT'} entangled with the rest of the system")
qc_mod, _, _ = hp_circuit2(scramble_depth=scramble_depth)
qc_mod.save_statevector()
result = sim.run(transpile(qc_mod, sim)).result()
rho = DensityMatrix(result.get_statevector())
S_q7_mod = entropy(partial_trace(rho, [0,1,2,3,4,5,6]), base=2)
print(f"\nCircuit2:")
print(f" S(q7) = {S_q7_mod:.4f} bits")
print(f" q7 {'IS' if S_q7_mod > 0.1 else 'IS NOT'} entangled with the rest of the system")
Circuit1: S(q7) = 0.8113 bits q7 IS entangled with the rest of the system Circuit2: S(q7) = 0.7892 bits q7 IS entangled with the rest of the system
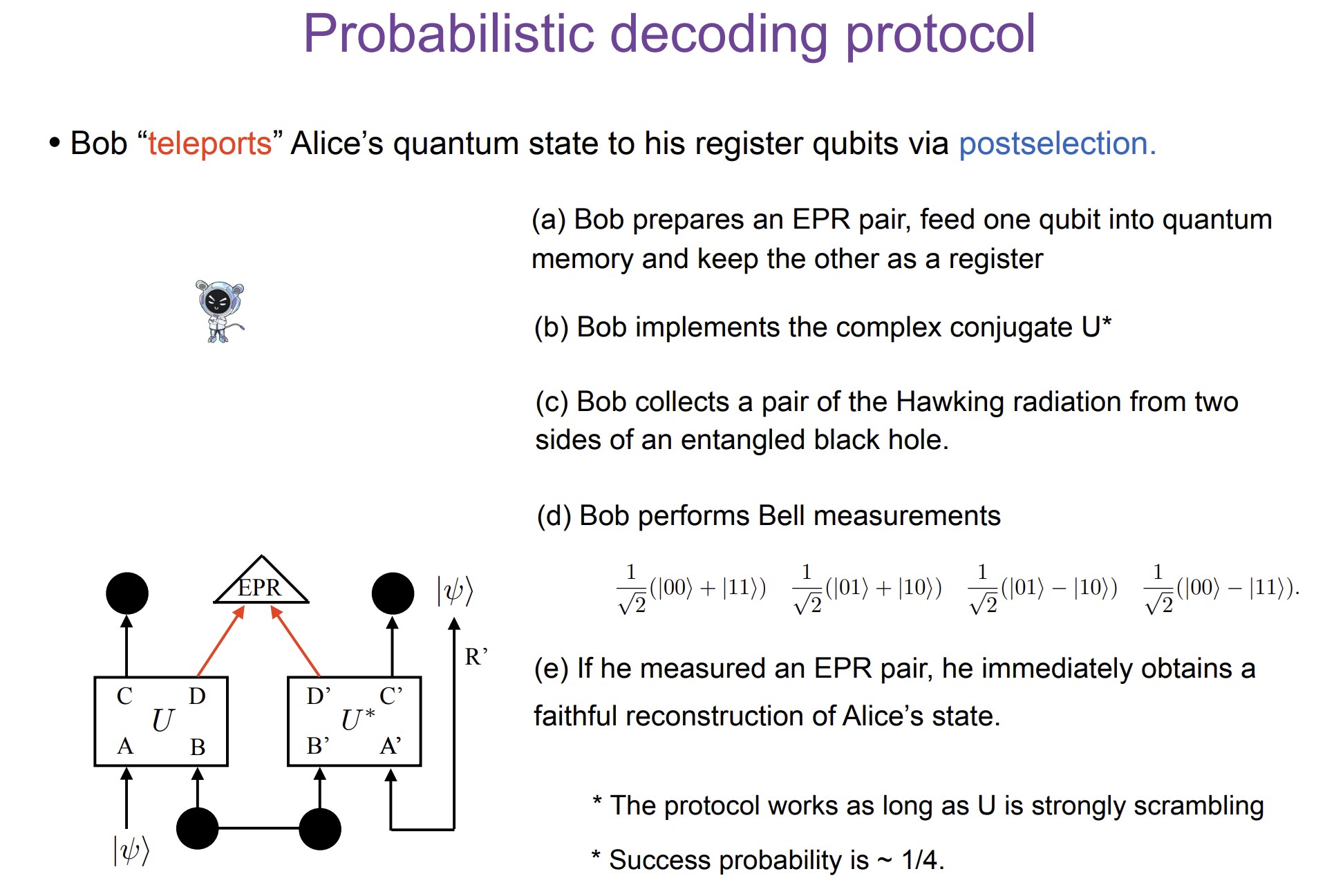
10. Probabilistic Decoding Protocol¶
Postselection Strategy¶
Bob "teleports" Alice's quantum state using:
- Scrambling: Unitary operation U entangles information with the rest of the black hole
- Radiation emission: Part of the information escapes in Hawking radiation
- Measurement: Bob measures correlations between:
- Left radiation (q6)
- Right radiation (q13)
Two Types of Measurements¶
A) Swap Test¶
- Measures overlap between two quantum states
- Success rate ~25% for maximally entangled states
- Suitable for verifying overall fidelity
B) Bell Measurement (EPR measurement)¶
- Measures specific Bell states (|Φ+⟩, |Φ-⟩, |Ψ+⟩, |Ψ-⟩)
- Theoretical success rate: ~25% (P_EPR ≈ 0.25)
- More precise test of quantum entanglement
- Directly tests the hypothesis about decoding possibility
Theoretical Results¶
For correct implementation of Yoshida-Kitaev protocol:
- P_EPR ≈ 0.25 (1/4) - corresponds to selecting one of 4 Bell states
- Swap test success: similar probability
- Any significant deviation indicates an error in implementation
def analyze_qubit_state(qc, qubit_indices, label=""):
"""Analyzes the reduced density matrix for given qubits."""
sim = AerSimulator(method='statevector')
qc_copy = qc.copy()
qc_copy.save_statevector()
result = sim.run(transpile(qc_copy, sim)).result()
statevector = result.get_statevector()
rho_full = DensityMatrix(statevector)
all_qubits = list(range(8))
trace_out = [q for q in all_qubits if q not in qubit_indices]
rho_reduced = partial_trace(rho_full, trace_out)
S = entropy(rho_reduced, base=2)
purity = np.trace(np.array(rho_reduced) @ np.array(rho_reduced)).real
return rho_reduced, S, purity
def compute_mutual_information(qc, qubits_A, qubits_B):
"""Computes I(A:B) = S(A) + S(B) - S(A,B)"""
sim = AerSimulator(method='statevector')
qc_copy = qc.copy()
qc_copy.save_statevector()
result = sim.run(transpile(qc_copy, sim)).result()
rho_full = DensityMatrix(result.get_statevector())
all_qubits = list(range(8))
# S(A)
trace_A = [q for q in all_qubits if q not in qubits_A]
rho_A = partial_trace(rho_full, trace_A)
S_A = entropy(rho_A, base=2)
# S(B)
trace_B = [q for q in all_qubits if q not in qubits_B]
rho_B = partial_trace(rho_full, trace_B)
S_B = entropy(rho_B, base=2)
# S(A,B)
qubits_AB = list(set(qubits_A + qubits_B))
trace_AB = [q for q in all_qubits if q not in qubits_AB]
rho_AB = partial_trace(rho_full, trace_AB)
S_AB = entropy(rho_AB, base=2)
I_AB = S_A + S_B - S_AB
return {'I(A:B)': I_AB, 'S(A)': S_A, 'S(B)': S_B, 'S(AB)': S_AB}
def run_swap_test(qc_base, qr, cr):
qc_decode = qc_base.copy()
# SWAP test: q7 controls swap between q6 and q5
qc_decode.cswap(qr[7], qr[6], qr[5])
qc_decode.h(qr[7])
# Measurement
qc_decode.measure(qr[7], cr[0]) # SWAP test result
qc_decode.measure(qr[6], cr[1]) # Decoded radiation
qc_decode.measure(qr[5], cr[2]) # Reference
sim = AerSimulator()
compiled = transpile(qc_decode, sim)
result = sim.run(compiled, shots=8192).result()
counts = result.get_counts()
return counts, qc_decode
def run_bell_measurement(qc_base):
qc_decode = qc_base.copy()
qr = qc_decode.qregs[0]
cr = ClassicalRegister(4, 'c_add')
qc_decode.add_register(cr)
# Measurement
qc_decode.cx(qr[6], qr[5])
qc_decode.h(qr[6])
qc_decode.measure(qr[5], cr[0])
qc_decode.measure(qr[6], cr[1])
qc_decode.measure(qr[0], cr[2])
qc_decode.measure(qr[7], cr[3])
sim = AerSimulator()
compiled = transpile(qc_decode, sim)
result = sim.run(compiled, shots=8192).result()
counts = result.get_counts()
return counts, qc_decode
11a. Decoding circuit 1¶
def hp_circuit_for_decoding():
"""
Hayden-Preskill circuit modified for decoding analysis.
We stop BEFORE the SWAP test.
"""
qr = QuantumRegister(8, 'q')
cr = ClassicalRegister(3, 'c')
qc = QuantumCircuit(qr, cr)
# === Initialization ===
qc.h(qr[5])
qc.h(qr[7])
qc.cx(qr[5], qr[0])
qc.cz(qr[0], qr[5])
qc.barrier(label='Bell A↔R')
qc.h(qr[0])
qc.barrier(label='BH init')
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[1])
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[2])
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[3])
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[4])
qc.barrier(label='q0→BH')
# === Scrambling - systematic CNOT cascades ===
for source in range(5):
for target in range(5):
if source != target:
qc.cx(qr[source], qr[target])
for i in range(5):
qc.rx(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.ry(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.rz(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.barrier(label='Scramble')
#qc.rx(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[3])
#qc.ry(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[3])
#qc.rz(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[3])
# === Hawking radiation - emission to q6 ===
qc.cx(qr[2], qr[6]) # q2 radiates
qc.h(2)
qc.cx(qr[3], qr[6]) # q3 radiates
qc.h(3)
qc.cx(qr[4], qr[6]) # q4 radiates
qc.h(4)
qc.h(qr[6]) # Hadamard on radiation
return qc, qr, cr
qc_base, qr, cr = hp_circuit_for_decoding()
qc_base.draw(output='mpl', fold=100)
print("[1] QUBIT STATE ANALYSIS")
for idx, name in [(6, "Radiation"), (5, "Reference"), (0, "Original info")]:
rho, S, purity = analyze_qubit_state(qc_base, [idx], name)
print(f"\nQubit {idx} ({name}):")
print(f" Von Neumann entropy: S = {S:.4f} bits")
print(f" Purity Tr(ρ²) = {purity:.4f}")
print(f" Density matrix ρ:")
print(f" {np.array2string(np.array(rho), precision=3, suppress_small=True)}")
print("\n[2] MUTUAL INFORMATION")
mi_rad_ref = compute_mutual_information(qc_base, [6], [5])
mi_rad_bh = compute_mutual_information(qc_base, [6], [0,1,2,3,4])
mi_ref_bh = compute_mutual_information(qc_base, [5], [0,1,2,3,4])
mi_radref_bh = compute_mutual_information(qc_base, [5,6], [0,1,2,3,4])
print(f"\nI(Radiation : Reference) = {mi_rad_ref['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits")
print(f"I(Radiation : Black hole) = {mi_rad_bh['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits")
print(f"I(Reference : Black hole) = {mi_ref_bh['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits")
print(f"I(Rad+Ref : Black hole) = {mi_radref_bh['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits ← Key!")
print("\n[3] SWAP TEST DECODING")
counts_swap, qc_swap = run_swap_test(qc_base, qr, cr)
swap_0 = 0
swap_1 = 0
print("\nResults (Ref|Rad|SwapTest):")
for state, count in sorted(counts_swap.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:8]:
prob = count / 8192
swap_bit = state[2]
if swap_bit == '0':
swap_0 += count
else:
swap_1 += count
print(f" |{state}⟩: {count:4d} ({prob:.3f})")
# Calculate the rest
for state, count in counts_swap.items():
if state not in [s for s, _ in sorted(counts_swap.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:8]]:
if state[2] == '0':
swap_0 += count
else:
swap_1 += count
fidelity = swap_0 / 8192
print(f"\nSWAP test |0⟩: {swap_0} ({swap_0/8192:.3f})")
print(f"SWAP test |1⟩: {swap_1} ({swap_1/8192:.3f})")
print(f"\n Estimated FIDELITY: F ≈ {fidelity:.3f}")
print(f" → F > 0.5 means successful decoding!")
print("\n[4] MEASUREMENT")
counts_bell, qc_bell = run_bell_measurement(qc_base)
bell_states = {'00': '|Φ+⟩', '01': '|Ψ+⟩', '10': '|Φ-⟩', '11': '|Ψ-⟩'}
bell_counts = {'00': 0, '01': 0, '10': 0, '11': 0}
print("\nResults (q7|q0|q6|q5):")
for state, count in sorted(counts_bell.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:8]:
prob = count / 8192
bell_bits = state[1] + state[0]
bell_counts[bell_bits] += count
print(f" |{state}⟩: {count:4d} ({prob:.3f}) - Bell: {bell_states.get(bell_bits, '?')}")
for state, count in counts_bell.items():
bell_bits = state[1] + state[0]
if state not in [s for s, _ in sorted(counts_bell.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:8]]:
bell_counts[bell_bits] += count
print(f"\nBell state distribution:")
for bs, name in bell_states.items():
print(f" {name}: {bell_counts[bs]:4d} ({bell_counts[bs]/8192:.3f})")
print("\n[5] VISUALIZATION")
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 4))
ax1 = axes[0]
labels = ['I(Rad:Ref)', 'I(Rad:BH)', 'I(Ref:BH)', 'I(Rad+Ref:BH)']
values = [
mi_rad_ref['I(A:B)'],
mi_rad_bh['I(A:B)'],
mi_ref_bh['I(A:B)'],
mi_radref_bh['I(A:B)']
]
colors = ['#6c74a4', '#bbb9bc', '#5e2424', '#95bb9a']
bars = ax1.bar(labels, values, color=colors, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax1.set_ylabel('Mutual Information [bits]', fontsize=11)
ax1.set_title('Quantum correlations', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax1.axhline(y=1.0, color='gray', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
for bar, val in zip(bars, values):
ax1.text(bar.get_x() + bar.get_width()/2, bar.get_height() + 0.03,
f'{val:.3f}', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10, fontweight='bold')
ax2 = axes[1]
bell_labels = list(bell_states.values())
bell_values = [bell_counts[bs]/8192 for bs in bell_states.keys()]
colors2 = ['#95bb9a', '#bbb9bc', '#bbb9bc', '#bbb9bc']
ax2.bar(bell_labels, bell_values, color=colors2, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax2.set_ylabel('Probability', fontsize=11)
ax2.set_title('Bell state distribution', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax2.axhline(y=0.25, color='gray', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5, label='Uniform')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.close()
print("\n[5] QUBIT 6 DECODING SUMMARY")
print(f"""
Qubit 6 (Hawking radiation) collects information from qubits 2, 3, 4.
• Von Neumann entropy S(q6) shows the degree of mixing
• I(Radiation : Reference) = {mi_rad_ref['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits
→ Correlation between radiation and original reference
• SWAP test fidelity: F ≈ {fidelity:.3f}
→ {'SUCCESSFUL' if fidelity > 0.5 else 'UNSUCCESSFUL'} decoding (F {'>' if fidelity > 0.5 else '<'} 0.5)
Key to decoding: I(Rad+Ref : BH) = {mi_radref_bh['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits
""")
[1] QUBIT STATE ANALYSIS
Qubit 6 (Radiation):
Von Neumann entropy: S = 0.9938 bits
Purity Tr(ρ²) = 0.5043
Density matrix ρ:
[[0.5 -0.j 0.046+0.j]
[0.046+0.j 0.5 -0.j]]
Qubit 5 (Reference):
Von Neumann entropy: S = 1.0000 bits
Purity Tr(ρ²) = 0.5000
Density matrix ρ:
[[ 0.5-0.j -0. -0.j]
[-0. +0.j 0.5-0.j]]
Qubit 0 (Original info):
Von Neumann entropy: S = 1.0000 bits
Purity Tr(ρ²) = 0.5000
Density matrix ρ:
[[ 0.5-0.j -0. +0.j]
[-0. -0.j 0.5-0.j]]
[2] MUTUAL INFORMATION
I(Radiation : Reference) = -0.0000 bits
I(Radiation : Black hole) = 1.9875 bits
I(Reference : Black hole) = 2.0000 bits
I(Rad+Ref : Black hole) = 3.9875 bits ← Key!
[3] SWAP TEST DECODING
Results (Ref|Rad|SwapTest):
|110⟩: 2096 (0.256)
|000⟩: 2041 (0.249)
|010⟩: 1034 (0.126)
|100⟩: 1022 (0.125)
|011⟩: 1022 (0.125)
|101⟩: 977 (0.119)
SWAP test |0⟩: 6193 (0.756)
SWAP test |1⟩: 1999 (0.244)
Estimated FIDELITY: F ≈ 0.756
→ F > 0.5 means successful decoding!
[4] MEASUREMENT
Results (q7|q0|q6|q5):
|0101 000⟩: 575 (0.070) - Bell: |Φ-⟩
|0100 000⟩: 562 (0.069) - Bell: |Φ-⟩
|0000 000⟩: 544 (0.066) - Bell: |Φ+⟩
|1011 000⟩: 527 (0.064) - Bell: |Ψ+⟩
|1100 000⟩: 526 (0.064) - Bell: |Ψ-⟩
|1110 000⟩: 518 (0.063) - Bell: |Ψ-⟩
|0110 000⟩: 503 (0.061) - Bell: |Φ-⟩
|1010 000⟩: 503 (0.061) - Bell: |Ψ+⟩
Bell state distribution:
|Φ+⟩: 1996 (0.244)
|Ψ+⟩: 2023 (0.247)
|Φ-⟩: 2134 (0.260)
|Ψ-⟩: 2039 (0.249)
[5] VISUALIZATION
[5] QUBIT 6 DECODING SUMMARY
Qubit 6 (Hawking radiation) collects information from qubits 2, 3, 4.
• Von Neumann entropy S(q6) shows the degree of mixing
• I(Radiation : Reference) = -0.0000 bits
→ Correlation between radiation and original reference
• SWAP test fidelity: F ≈ 0.756
→ SUCCESSFUL decoding (F > 0.5)
Key to decoding: I(Rad+Ref : BH) = 3.9875 bits
11b. Decoding circuit 2¶
def hp_circuit_for_decoding2(scramble_depth=scramble_depth):
"""
Hayden-Preskill circuit modified for decoding analysis.
We stop BEFORE the SWAP test.
"""
qr = QuantumRegister(8, 'q')
cr = ClassicalRegister(3, 'c')
qc = QuantumCircuit(qr, cr)
qc.h(qr[5])
qc.h(qr[7])
qc.cx(qr[5], qr[0])
qc.cz(qr[0], qr[5])
qc.barrier(label='Bell q0↔q5')
qc.h(qr[0])
#for i in range(0, 5):
# qc.h(qr[i])
qc.barrier(label='BH init')
for i in range(1, 5):
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[i])
qc.barrier(label='q0→BH')
for layer in range(scramble_depth):
# Random single-qubit rotations on BH (q0-q4)
for i in range(5):
qc.rx(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.ry(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
qc.rz(np.random.uniform(0, 2*np.pi), qr[i])
# CNOT layer (forward) - only within BH
for i in range(4):
qc.cx(qr[i], qr[i+1])
# CNOT layer (backward)
for i in range(3, -1, -1):
qc.cx(qr[i+1], qr[i])
qc.barrier(label='Scramble')
qc.cx(qr[2], qr[6])
qc.h(2)
qc.cx(qr[3], qr[6])
qc.h(3)
qc.cx(qr[4], qr[6])
qc.h(4)
qc.h(qr[6])
return qc, qr, cr
qc_base, qr, cr = hp_circuit_for_decoding2()
qc_base.draw(output='mpl', fold=100)
print("[1] QUBIT STATE ANALYSIS")
for idx, name in [(6, "Radiation"), (5, "Reference"), (0, "Original info")]:
rho, S, purity = analyze_qubit_state(qc_base, [idx], name)
print(f"\nQubit {idx} ({name}):")
print(f" Von Neumann entropy: S = {S:.4f} bits")
print(f" Purity Tr(ρ²) = {purity:.4f}")
print(f" Density matrix ρ:")
print(f" {np.array2string(np.array(rho), precision=3, suppress_small=True)}")
print("\n[2] MUTUAL INFORMATION")
mi_rad_ref = compute_mutual_information(qc_base, [6], [5])
mi_rad_bh = compute_mutual_information(qc_base, [6], [0,1,2,3,4])
mi_ref_bh = compute_mutual_information(qc_base, [5], [0,1,2,3,4])
mi_radref_bh = compute_mutual_information(qc_base, [5,6], [0,1,2,3,4])
print(f"\nI(Radiation : Reference) = {mi_rad_ref['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits")
print(f"I(Radiation : Black hole) = {mi_rad_bh['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits")
print(f"I(Reference : Black hole) = {mi_ref_bh['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits")
print(f"I(Rad+Ref : Black hole) = {mi_radref_bh['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits ← Key!")
print("\n[3] SWAP TEST DECODING")
counts_swap, qc_swap = run_swap_test(qc_base, qr, cr)
swap_0 = 0
swap_1 = 0
print("\nResults (Ref|Rad|SwapTest):")
for state, count in sorted(counts_swap.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:8]:
prob = count / 8192
swap_bit = state[2]
if swap_bit == '0':
swap_0 += count
else:
swap_1 += count
print(f" |{state}⟩: {count:4d} ({prob:.3f})")
# Calculate the rest
for state, count in counts_swap.items():
if state not in [s for s, _ in sorted(counts_swap.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:8]]:
if state[2] == '0':
swap_0 += count
else:
swap_1 += count
fidelity = swap_0 / 8192
print(f"\nSWAP test |0⟩: {swap_0} ({swap_0/8192:.3f})")
print(f"SWAP test |1⟩: {swap_1} ({swap_1/8192:.3f})")
print(f"\n Estimated FIDELITY: F ≈ {fidelity:.3f}")
print(f" → F > 0.5 means successful decoding!")
print("\n[4] MEASUREMENT")
counts_bell, qc_bell = run_bell_measurement(qc_base)
bell_states = {'00': '|Φ+⟩', '01': '|Ψ+⟩', '10': '|Φ-⟩', '11': '|Ψ-⟩'}
bell_counts = {'00': 0, '01': 0, '10': 0, '11': 0}
print("\nResults (q7|q0|q6|q5):")
for state, count in sorted(counts_bell.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:8]:
prob = count / 8192
bell_bits = state[1] + state[0]
bell_counts[bell_bits] += count
print(f" |{state}⟩: {count:4d} ({prob:.3f}) - Bell: {bell_states.get(bell_bits, '?')}")
for state, count in counts_bell.items():
bell_bits = state[1] + state[0]
if state not in [s for s, _ in sorted(counts_bell.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:8]]:
bell_counts[bell_bits] += count
print(f"\nBell state distribution:")
for bs, name in bell_states.items():
print(f" {name}: {bell_counts[bs]:4d} ({bell_counts[bs]/8192:.3f})")
print("\n[5] VISUALIZATION")
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 4))
ax1 = axes[0]
labels = ['I(Rad:Ref)', 'I(Rad:BH)', 'I(Ref:BH)', 'I(Rad+Ref:BH)']
values = [
mi_rad_ref['I(A:B)'],
mi_rad_bh['I(A:B)'],
mi_ref_bh['I(A:B)'],
mi_radref_bh['I(A:B)']
]
colors = ['#6c74a4', '#bbb9bc', '#5e2424', '#95bb9a']
bars = ax1.bar(labels, values, color=colors, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax1.set_ylabel('Mutual Information [bits]', fontsize=11)
ax1.set_title('Quantum correlations', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax1.axhline(y=1.0, color='gray', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
for bar, val in zip(bars, values):
ax1.text(bar.get_x() + bar.get_width()/2, bar.get_height() + 0.03,
f'{val:.3f}', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10, fontweight='bold')
ax2 = axes[1]
bell_labels = list(bell_states.values())
bell_values = [bell_counts[bs]/8192 for bs in bell_states.keys()]
colors2 = ['#95bb9a', '#bbb9bc', '#bbb9bc', '#bbb9bc']
ax2.bar(bell_labels, bell_values, color=colors2, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax2.set_ylabel('Probability', fontsize=11)
ax2.set_title('Bell state distribution', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax2.axhline(y=0.25, color='gray', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5, label='Uniform')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.close()
print("\n[5] QUBIT 6 DECODING SUMMARY")
print(f"""
Qubit 6 (Hawking radiation) collects information from qubits 2, 3, 4.
• Von Neumann entropy S(q6) shows the degree of mixing
• I(Radiation : Reference) = {mi_rad_ref['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits
→ Correlation between radiation and original reference
• SWAP test fidelity: F ≈ {fidelity:.3f}
→ {'SUCCESSFUL' if fidelity > 0.5 else 'UNSUCCESSFUL'} decoding (F {'>' if fidelity > 0.5 else '<'} 0.5)
Key to decoding: I(Rad+Ref : BH) = {mi_radref_bh['I(A:B)']:.4f} bits
""")
[1] QUBIT STATE ANALYSIS
Qubit 6 (Radiation):
Von Neumann entropy: S = 0.9968 bits
Purity Tr(ρ²) = 0.5022
Density matrix ρ:
[[0.5 -0.j 0.033-0.j]
[0.033-0.j 0.5 -0.j]]
Qubit 5 (Reference):
Von Neumann entropy: S = 1.0000 bits
Purity Tr(ρ²) = 0.5000
Density matrix ρ:
[[ 0.5+0.j -0. -0.j]
[-0. +0.j 0.5-0.j]]
Qubit 0 (Original info):
Von Neumann entropy: S = 0.9712 bits
Purity Tr(ρ²) = 0.5198
Density matrix ρ:
[[ 0.552-0.j -0.059+0.061j]
[-0.059-0.061j 0.448+0.j ]]
[2] MUTUAL INFORMATION
I(Radiation : Reference) = 0.0074 bits
I(Radiation : Black hole) = 1.9862 bits
I(Reference : Black hole) = 1.9926 bits
I(Rad+Ref : Black hole) = 3.9788 bits ← Key!
[3] SWAP TEST DECODING
Results (Ref|Rad|SwapTest):
|110⟩: 2057 (0.251)
|000⟩: 2031 (0.248)
|010⟩: 1109 (0.135)
|100⟩: 1095 (0.134)
|101⟩: 968 (0.118)
|011⟩: 932 (0.114)
SWAP test |0⟩: 6292 (0.768)
SWAP test |1⟩: 1900 (0.232)
Estimated FIDELITY: F ≈ 0.768
→ F > 0.5 means successful decoding!
[4] MEASUREMENT
Results (q7|q0|q6|q5):
|1000 000⟩: 655 (0.080) - Bell: |Ψ+⟩
|0001 000⟩: 623 (0.076) - Bell: |Φ+⟩
|0000 000⟩: 623 (0.076) - Bell: |Φ+⟩
|1001 000⟩: 618 (0.075) - Bell: |Ψ+⟩
|1011 000⟩: 550 (0.067) - Bell: |Ψ+⟩
|0010 000⟩: 526 (0.064) - Bell: |Φ+⟩
|0011 000⟩: 512 (0.062) - Bell: |Φ+⟩
|1010 000⟩: 491 (0.060) - Bell: |Ψ+⟩
Bell state distribution:
|Φ+⟩: 2284 (0.279)
|Ψ+⟩: 2314 (0.282)
|Φ-⟩: 1790 (0.219)
|Ψ-⟩: 1804 (0.220)
[5] VISUALIZATION
[5] QUBIT 6 DECODING SUMMARY
Qubit 6 (Hawking radiation) collects information from qubits 2, 3, 4.
• Von Neumann entropy S(q6) shows the degree of mixing
• I(Radiation : Reference) = 0.0074 bits
→ Correlation between radiation and original reference
• SWAP test fidelity: F ≈ 0.768
→ SUCCESSFUL decoding (F > 0.5)
Key to decoding: I(Rad+Ref : BH) = 3.9788 bits
12. Back to Information Loss - Modern Interpretation¶
Revision of Black Hole Complementarity¶
Old View:
- Information falling into a black hole is lost
- It's impossible to retrieve it
- Apparent conflict with unitarity
Modern Interpretation (post Hayden-Preskill):
There is no quantum cloning, BUT an object can be pulled back from a black hole!
Key Conclusions:
- Information is not lost - it's merely "scrambled"
- After Page time, information rapidly appears in Hawking radiation
- With sufficient quantum memory (Bob's memory M), information can be decoded
- The process is probabilistic but has non-zero success probability
Physical Implications¶
Scrambling time:
- Characteristic time for information to disperse throughout the black hole
- For black holes: t_scramble ~ (M/ℏ)log(S), where S is entropy
- Quantum experiments: several scrambling steps
13. State-Channel Duality (Choi-Jamiłkowski Isomorphism)¶
Key Mathematical Concept¶
Basic Idea:
A unitary operator U acting on n qubits can be viewed as a quantum state on 2n qubits.
Mathematically: $$ \begin{aligned} U &= \sum_{i,j} U_{ij} |i\rangle\langle j| \end{aligned} $$
This duality enables:
- Converting dynamics (operator) into a static quantum state
- Connecting quantum circuits with entangled states
- Implementing "teleportation" of quantum information through scrambled systems
Practical Significance:
- The scrambling operation in a black hole (represented by unitary U) can be encoded as an entangled state
- Bob can use this state to decode Alice's information
14. Yoshida-Kitaev Protocol for Eternal Black Holes¶
Protocol Structure¶
Quantum Registers:¶
LEFT side: q0-q4 (5 qubits)
q0: Hadamard (Alice's qubit "falling in")
q1-q4: Scrambling unitary U
CENTER: q5-q7 (3 qubits)
q5: center
q6: left radiation
q7: entanglement witness
RIGHT side: q8-q12 (5 qubits)
q8: Hadamard (mirror of Alice's qubit)
q9-q12: Adjoint scrambling U†
Symmetry and Adjoint Operation¶
CRITICALLY IMPORTANT: Implementation of the adjoint operator U† requires:
- Negated rotation angles: θ → -θ
- Reversed gate order: the last gate becomes the first
- Transposed CNOT structures: control ↔ target
Why is CNOT transposition important?
LEFT side: CNOT(control: qi, target: qj)
RIGHT side: CNOT(control: qj, target: qi) ← swapped!
This transposition ensures a mathematically correct adjoint operation, which is essential for successful decoding.
Thermofield Double State¶
For eternal black hole:
$$ \begin{aligned} |TFD\rangle &= \frac{1}{\sqrt{d}} \sum_{i} |i\rangle_L \otimes |i\rangle_R \end{aligned} $$
This state represents a maximally entangled system between the LEFT and RIGHT sides of the black hole.
def create_yoshida_eternal_bh(scramble_depth=scramble_depth, seed=m_rnd_value):
"""
Creates a quantum circuit for the Yoshida-Kitaev eternal black hole protocol.
Qubit structure:
- q0-q4: LEFT black hole (5 qubits)
- q5: Reference qubit A (for Bell pair with q0)
- q6: Radiation qubit (Hawking radiation)
- q7: Auxiliary qubit
- q8-q12: RIGHT black hole (5 qubits, mirror side)
Parameters:
scramble_depth: Number of scrambling operation layers
seed: Random seed for reproducibility
"""
np.random.seed(seed)
qr = QuantumRegister(13, 'q')
qc = QuantumCircuit(qr)
# BELL PAIR PREPARATION (A ↔ R)
# Create maximally entangled Bell state between reference A (q5) and input R (q0)
# This pair represents information "falling" into the black hole
qc.h(qr[5])
qc.h(qr[7])
qc.cx(qr[5], qr[0])
qc.cz(qr[0], qr[5])
qc.barrier(label='Bell A↔R')
# QUBIT "FALLS" INTO BLACK HOLE
# Hadamard on q0 simulates the physical process of qubit falling into black hole
# CRITICAL: This operation must be preserved - represents interaction with event horizon
qc.h(qr[0])
# DISTRIBUTION INTO LEFT BLACK HOLE
# Input qubit q0 "spreads" into entire LEFT system (q0-q4)
# This creates initial entanglement structure before scrambling operations
for i in range(1, 5):
qc.cx(qr[0], qr[i])
qc.barrier(label='A→BH_L')
# SCRAMBLING OPERATIONS (LEFT SIDE)
# Generate and apply chaotic unitary transformation U on LEFT system
# This operation simulates thermalization and "loss" of information in black hole
rotation_angles = [] # Store angles for later adjoint operation
cnot_sequence = [] # Store CNOT sequence for transposition
for layer in range(scramble_depth):
# Random single-qubit rotations on all LEFT qubits
layer_angles = []
for i in range(5):
angles = (np.random.uniform(0, 2 * np.pi),
np.random.uniform(0, 2 * np.pi),
np.random.uniform(0, 2 * np.pi))
layer_angles.append(angles)
qc.rx(angles[0], qr[i])
qc.ry(angles[1], qr[i])
qc.rz(angles[2], qr[i])
rotation_angles.append(layer_angles)
# CNOT forward (creates entanglement between neighboring qubits)
cnot_fwd = []
for i in range(4):
qc.cx(qr[i], qr[i + 1])
cnot_fwd.append((i, i + 1))
# CNOT backward (second layer for complete scrambling)
cnot_bwd = []
for i in range(3, -1, -1):
qc.cx(qr[i + 1], qr[i])
cnot_bwd.append((i + 1, i))
cnot_sequence.append((cnot_fwd, cnot_bwd))
qc.barrier(label='Scramble_L')
# Create maximal entanglement between LEFT (q0-q4) and RIGHT (q8-q12)
# This is key for eternal black hole - connecting two asymptotic regions
for i in range(5):
qc.cx(qr[i], qr[8 + i])
# ADJOINT OPERATION U† (RIGHT SIDE)
# Apply inverse operation on RIGHT system
# CRITICAL IMPLEMENTATION DETAILS:
# 1. Reversed layer order (reversed range)
# 2. Negated rotation angles (-angles)
# 3. TRANSPOSED CNOT OPERATIONS (swapped control/target)
# - LEFT: cx(i, i+1) → RIGHT: cx(i+1+8, i+8)
# - This is mathematically correct adjoint for CNOT structure
for layer in reversed(range(scramble_depth)):
cnot_fwd, cnot_bwd = cnot_sequence[layer]
# Reverse CNOT backward with TRANSPOSED qubits
# LEFT had cx(i+1, i) → RIGHT has cx(i+8, i+1+8)
for ctrl, targ in reversed(cnot_bwd):
qc.cx(qr[targ + 8], qr[ctrl + 8]) # SWAP control ↔ target!
# Reverse CNOT forward with TRANSPOSED qubits
# LEFT had cx(i, i+1) → RIGHT has cx(i+1+8, i+8)
for ctrl, targ in reversed(cnot_fwd):
qc.cx(qr[targ + 8], qr[ctrl + 8]) # SWAP control ↔ target!
# Inverse rotations (negated angles in opposite order RZ-RY-RX)
layer_angles = rotation_angles[layer]
for i in reversed(range(5)):
angles = layer_angles[i]
qc.rz(-angles[2], qr[i + 8])
qc.ry(-angles[1], qr[i + 8])
qc.rx(-angles[0], qr[i + 8])
qc.barrier(label='Scramble_R')
# Extract information from both systems into radiation qubit q6
# From LEFT system (q2, q3, q4 → q6)
# This simulates emission of "late" Hawking radiation that no longer contains information
qc.cx(qr[2], qr[6])
qc.h(2)
qc.cx(qr[3], qr[6])
qc.h(3)
qc.cx(qr[4], qr[6])
qc.h(4)
# From RIGHT system (q10, q11, q12 → q6)
# This is CRITICAL: RIGHT system preserves information due to adjoint operation U†
# Therefore radiation from RIGHT side can restore original entanglement with reference A
qc.cx(qr[10], qr[6])
qc.h(10)
qc.cx(qr[11], qr[6])
qc.h(11)
qc.cx(qr[12], qr[6])
qc.h(12)
# Final Hadamard on radiation qubit
qc.h(qr[6])
qc.barrier(label='Radiation')
return qc, qr
def run_bell_measurements(qc, qr):
"""
Bell pair measurements for eternal BH - tests Hayden-Preskill information recovery.
Two key tests:
1. Original Bell (q5 ↔ q0): Measures entanglement reference A vs LEFT input R
- Expected LOW P_EPR (information lost by scrambling in LEFT)
2. Cross-side (q5 ↔ q8): Measures entanglement reference A vs RIGHT input R'
- Expected HIGH P_EPR ≥ 0.25 (information restored due to U†)
- This is proof of Hayden-Preskill protocol!
"""
results = {}
sim = AerSimulator()
# Measures remaining entanglement between reference A (q5) and LEFT input R (q0)
# After scrambling this should be almost destroyed
qc_orig = qc.copy()
cr_o = ClassicalRegister(2, 'c_original')
qc_orig.add_register(cr_o)
# Bell measurement: CNOT + Hadamard + measure
qc_orig.cx(qr[5], qr[0])
qc_orig.h(qr[5])
qc_orig.measure(qr[5], cr_o[0])
qc_orig.measure(qr[0], cr_o[1])
result_o = sim.run(transpile(qc_orig, sim), shots=8192).result()
counts_o = result_o.get_counts()
# Aggregate into Bell basis {|Φ+⟩, |Ψ+⟩, |Φ-⟩, |Ψ-⟩}
bell_o = {'00': 0, '01': 0, '10': 0, '11': 0}
for state, count in counts_o.items():
bell_bits = state[-2] + state[-1] # Last 2 bits
bell_o[bell_bits] += count
results['original'] = bell_o
# Measures entanglement between reference A (q5) and RIGHT input R' (q8)
# Due to adjoint operation U† on RIGHT, entanglement should be RESTORED
# This is core of Hayden-Preskill: information appears on "other side"
qc_cross = qc.copy()
cr_c = ClassicalRegister(2, 'c_cross')
qc_cross.add_register(cr_c)
# Bell measurement: CNOT + Hadamard + measure
qc_cross.cx(qr[5], qr[8])
qc_cross.h(qr[5])
qc_cross.measure(qr[5], cr_c[0])
qc_cross.measure(qr[8], cr_c[1])
result_c = sim.run(transpile(qc_cross, sim), shots=8192).result()
counts_c = result_c.get_counts()
# Aggregate into Bell basis
bell_c = {'00': 0, '01': 0, '10': 0, '11': 0}
for state, count in counts_c.items():
bell_bits = state[-2] + state[-1]
bell_c[bell_bits] += count
results['cross'] = bell_c
return results
def run_swap_test_0_8(qc, qr):
"""
Swap test between q0 (LEFT) and q8 (RIGHT) - measures their fidelity/entanglement.
This test verifies that LEFT↔RIGHT entanglement is maximal.
High fidelity (> 0.95) confirms that both systems are in the same
quantum state, which is prerequisite for successful information recovery.
Fidelity calculation: F = 2*P(|0⟩) - 1
"""
qc_swap = qc.copy()
ancilla = QuantumRegister(1, 'ancilla')
qc_swap.add_register(ancilla)
cr = ClassicalRegister(1, 'c_swap')
qc_swap.add_register(cr)
# Standard swap test protocol
qc_swap.h(ancilla[0])
qc_swap.cswap(ancilla[0], qr[0], qr[8]) # Controlled-SWAP
qc_swap.h(ancilla[0])
qc_swap.measure(ancilla[0], cr[0])
sim = AerSimulator()
result = sim.run(transpile(qc_swap, sim), shots=8192).result()
counts = result.get_counts()
# Fidelity from probability of measuring |0⟩
p_0 = counts.get('0', 0) / 8192
fidelity = 2 * p_0 - 1
return fidelity, counts
def bell_swap_tests(qc, qr):
"""
Complete test suite for eternal BH validation:
1. Original Bell (q5 ↔ q0): Measures information loss in LEFT system
→ Expected P_EPR << 0.25 (information lost)
2. Cross-side (q5 ↔ q8): Measures information recovery in RIGHT system
→ Expected P_EPR ≥ 0.25 (information restored)
3. Swap test (q0 ↔ q8): Measures quality of LEFT↔RIGHT entanglement
→ Expected fidelity > 0.95 (maximal entanglement)
All three tests must pass for successful validation of Hayden-Preskill protocol.
"""
results = {}
sim = AerSimulator()
qc_orig = qc.copy()
cr_o = ClassicalRegister(2, 'c_original')
qc_orig.add_register(cr_o)
qc_orig.cx(qr[5], qr[0])
qc_orig.h(qr[5])
qc_orig.measure(qr[5], cr_o[0])
qc_orig.measure(qr[0], cr_o[1])
result_o = sim.run(transpile(qc_orig, sim), shots=8192).result()
counts_o = result_o.get_counts()
bell_o = {'00': 0, '01': 0, '10': 0, '11': 0}
for state, count in counts_o.items():
bell_bits = state[-2] + state[-1]
bell_o[bell_bits] += count
results['original'] = bell_o
qc_cross = qc.copy()
cr_c = ClassicalRegister(2, 'c_cross')
qc_cross.add_register(cr_c)
qc_cross.cx(qr[5], qr[8])
qc_cross.h(qr[5])
qc_cross.measure(qr[5], cr_c[0])
qc_cross.measure(qr[8], cr_c[1])
result_c = sim.run(transpile(qc_cross, sim), shots=8192).result()
counts_c = result_c.get_counts()
bell_c = {'00': 0, '01': 0, '10': 0, '11': 0}
for state, count in counts_c.items():
bell_bits = state[-2] + state[-1]
bell_c[bell_bits] += count
results['cross'] = bell_c
fidelity, swap_counts = run_swap_test_0_8(qc, qr)
results['swap'] = {'fidelity': fidelity, 'counts': swap_counts}
return results
qc_yoshida, qr = create_yoshida_eternal_bh(scramble_depth=scramble_depth)
qc_yoshida.draw(output='mpl', fold=80, scale=0.9)
results = bell_swap_tests(qc_yoshida, qr)
# Mapping bit strings to Bell states
bell_states = {'00': '|Φ+⟩', '01': '|Ψ+⟩', '10': '|Φ-⟩', '11': '|Ψ-⟩'}
for key, name in [('original', 'Original Bell (A ↔ R) - q5↔q0 [LOSS]'),
('cross', 'Cross-side (A ↔ R\') - q5↔q8 [RECOVERY]')]:
bell_counts = results[key]
total = sum(bell_counts.values())
print(f"\n{name}:")
for bs, bell_name in bell_states.items():
prob = bell_counts[bs] / total
# '00' corresponds to |Φ+⟩ - maximally entangled Bell state
success = ' ✓' if bs == '00' else ''
print(f" {bell_name}: {bell_counts[bs]:4d} ({prob:.4f}) {bar}{success}")
# P_EPR is probability of measuring |Φ+⟩ state
# Theoretical threshold for successful recovery: P_EPR ≥ 0.25
p_epr = bell_counts['00'] / total
status = "SUCCESS" if p_epr >= 0.25 else "FAILED"
print(f"P_EPR = {p_epr:.4f} [{status}]")
print("Swap Test (q0 ↔ q8):")
fidelity = results['swap']['fidelity']
swap_counts = results['swap']['counts']
p_0 = swap_counts.get('0', 0) / 8192
p_1 = swap_counts.get('1', 0) / 8192
print(f" |0⟩: {swap_counts.get('0', 0):4d} ({p_0:.4f})")
print(f" |1⟩: {swap_counts.get('1', 0):4d} ({p_1:.4f})")
print(f"\nFidelity = {fidelity:.4f}")
print(f"Status: {'BETTER ENTANGLEMENT' if fidelity > 0.8 else 'WORST ENTANGLEMENT'}")
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
gs = fig.add_gridspec(1, 3, width_ratios=[1, 1, 1])
# Plots for Bell measurements
for idx, (key, name) in enumerate([('original', 'Original Bell (A ↔ R)\nq5↔q0 [LOSS]'),
('cross', 'Cross-side (A ↔ R\')\nq5↔q8 [RECOVERY]')]):
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[idx])
bell_counts = results[key]
total = sum(bell_counts.values())
labels = list(bell_states.values())
values = [bell_counts[bs]/total for bs in ['00', '01', '10', '11']]
# Green for |Φ+⟩ (success), gray for others
colors = ['#95bb9a' if bs == '00' else '#bbb9bc' for bs in ['00', '01', '10', '11']]
ax.bar(labels, values, color=colors, edgecolor='black', linewidth=2)
# Red line at 0.25 = theoretical threshold for success
ax.axhline(y=0.25, color='red', linestyle='--', label='Threshold 0.25')
ax.set_ylabel('Probability')
ax.set_title(name)
ax.legend()
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
# Plot for Swap test
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[2])
swap_counts = results['swap']['counts']
labels = ['|0⟩', '|1⟩']
values = [swap_counts.get('0', 0)/8192, swap_counts.get('1', 0)/8192]
colors = ['#95bb9a', '#bbb9bc']
ax.bar(labels, values, color=colors, edgecolor='black', linewidth=2)
ax.set_ylabel('Probability')
ax.set_title(f'Swap Test q0↔q8\nFidelity = {fidelity:.4f}')
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Original Bell (A ↔ R) - q5↔q0 [LOSS]: |Φ+⟩: 1552 (0.1895) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) ✓ |Ψ+⟩: 1565 (0.1910) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) |Φ-⟩: 2505 (0.3058) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) |Ψ-⟩: 2570 (0.3137) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) P_EPR = 0.1895 [FAILED] Cross-side (A ↔ R') - q5↔q8 [RECOVERY]: |Φ+⟩: 2231 (0.2723) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) ✓ |Ψ+⟩: 2013 (0.2457) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) |Φ-⟩: 2023 (0.2469) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) |Ψ-⟩: 1925 (0.2350) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) P_EPR = 0.2723 [SUCCESS] Swap Test (q0 ↔ q8): |0⟩: 6471 (0.7899) |1⟩: 1721 (0.2101) Fidelity = 0.5798 Status: WORST ENTANGLEMENT
16. And now extended scrambling circuit with RXX gates and my class for forward and inversed scrambling generator¶
1. Create Scrambler¶
from scrambling_circuit import ScramblingCircuit
# Basic scrambler (5 qubits, 3 layers, starting from qubit 0)
scrambler = ScramblingCircuit(n_qubits=5, n_layers=3, seed=42, qubit_offset=0)
2. Generate Circuits¶
# Forward scrambling
forward_qc = scrambler.generate_scrambling_circuit()
# Inverse scrambling (after generating forward)
inverse_qc = scrambler.generate_inverse_circuit()
3. Visualization¶
# Forward circuit
scrambler.draw_forward_circuit(fold=30)
# Inverse circuit
scrambler.draw_inverse_circuit(fold=30)
# Complete analysis (6 plots)
scrambler.visualize_analysis()
4. Export/Import Configuration¶
# Export to JSON
jqc = scrambler.generate()
scrambler.to_json('scrambling_config.json')
# Import from JSON
loaded = ScramblingCircuit.from_json('scrambling_config.json')
5. Apply with Offset¶
# Scrambling starts from qubit 1 (instead of 0)
scrambler = ScramblingCircuit(n_qubits=5, n_layers=3, seed=42, qubit_offset=1)
# Create circuit with 10 qubits
qc = QuantumCircuit(10)
# Forward on qubits 1-5
fwd = ScramblingCircuit(5, 3, seed=42, qubit_offset=1)
qc.compose(fwd.generate_scrambling_circuit(total_qubits=10), inplace=True)
# Inverse on qubits 6-10
inv = ScramblingCircuit(5, 3, seed=100, qubit_offset=6)
_ = inv.generate_scrambling_circuit(total_qubits=10) # Generate parameters
qc.compose(inv.generate_inverse_circuit(total_qubits=10), inplace=True)
Parameters¶
__init__(n_qubits, n_layers, seed, qubit_offset)¶
- n_qubits (int): Number of qubits for scrambling (default: 5)
- n_layers (int): Number of scrambling layers (default: 3)
- seed (int): Random seed for reproducibility (default: None)
- qubit_offset (int): Starting qubit index (default: 0)
Methods¶
Circuit Generation¶
generate_scrambling_circuit(total_qubits=None)- Forward scramblinggenerate_inverse_circuit(total_qubits=None)- Inverse scramblingget_parameters()- Get stored rotation parametersset_parameters(params)- Set rotation parameters
Visualization¶
draw_forward_circuit(style, fold, save_path, total_qubits)- Draw forward circuitdraw_inverse_circuit(style, fold, save_path, total_qubits)- Draw inverse circuitvisualize_analysis(save_path)- Complete analysis (6 plots)
Export/Import¶
generate()- Generate JSON definitionto_json(filepath)- Export to JSON filefrom_json(filepath_or_dict)- Import from JSON (static method)
Scrambling Layer Structure¶
Each layer contains:
- RXX(π/2) gates between adjacent qubits
- RY(θ) + RZ(φ) random rotations on each qubit
- RXX(π/2) gates with shifted pattern (even-odd pairs)
- Barrier for clarity
Example: Asymmetric Scrambling¶
# Circuit with 15 qubits
qc = QuantumCircuit(15)
# Scrambling at different positions
s1 = ScramblingCircuit(5, 3, seed=42, qubit_offset=0) # qubits 0-4
s2 = ScramblingCircuit(5, 3, seed=123, qubit_offset=5) # qubits 5-9
s3 = ScramblingCircuit(5, 3, seed=456, qubit_offset=10) # qubits 10-14
# Apply
qc.compose(s1.generate_scrambling_circuit(15), inplace=True)
qc.compose(s2.generate_scrambling_circuit(15), inplace=True)
qc.compose(s3.generate_scrambling_circuit(15), inplace=True)
qc.draw('mpl', fold=40)
Invertibility Test¶
# Create test circuit
test_qc = QuantumCircuit(5)
# Forward + Inverse
scrambler = ScramblingCircuit(5, 3, seed=42)
test_qc.compose(scrambler.generate_scrambling_circuit(), inplace=True)
test_qc.compose(scrambler.generate_inverse_circuit(), inplace=True)
# Calculate fidelity with identity
from qiskit.quantum_info import Operator
U = Operator(test_qc).data
fidelity = abs(np.trace(U @ np.eye(32).conj().T)) / 32
print(f"Fidelity: {fidelity:.10f}") # Expected: ~1.0000000000
Notes¶
- Scrambling parameters are generated on first call to
generate_scrambling_circuit() - Inverse circuit requires prior forward generation (for parameters)
- Always set
seedfor reproducibility - Qubit offset enables scrambling application anywhere in the circuit
- JSON contains all rotation angles for precise reconstruction
qrE = QuantumRegister(13, 'q')
qcE = QuantumCircuit(qrE)
qcE.h(qrE[5])
qcE.h(qrE[7])
qcE.cx(qrE[5], qrE[0])
qcE.cz(qrE[0], qrE[5])
qcE.barrier(label='Bell A↔R')
qcE.h(qrE[0])
for i in range(1, 5):
qcE.cx(qrE[0], qrE[i])
qcE.barrier(label='A→BH_L')
scrambler_fwd = ScramblingCircuit(n_qubits=5, n_layers=3, seed=42, qubit_offset=0)
fwd_circuit = scrambler_fwd.generate_scrambling_circuit(total_qubits=13)
qcE.compose(fwd_circuit, inplace=True)
qcE.barrier(label='Scramble_L')
for i in range(5):
qcE.cx(qrE[i], qrE[8 + i])
scrambler_inv = ScramblingCircuit(n_qubits=5, n_layers=3, seed=42, qubit_offset=8)
_ = scrambler_inv.generate_scrambling_circuit(total_qubits=13)
inv_circuit = scrambler_inv.generate_inverse_circuit(total_qubits=13)
qcE.compose(inv_circuit, inplace=True)
qcE.barrier(label='Scramble_R')
qcE.cx(qrE[2], qrE[6])
qcE.h(2)
qcE.cx(qrE[3], qrE[6])
qcE.h(3)
qcE.cx(qrE[4], qrE[6])
qcE.h(4)
qcE.cx(qrE[10], qrE[6])
qcE.h(10)
qcE.cx(qrE[11], qrE[6])
qcE.h(11)
qcE.cx(qrE[12], qrE[6])
qcE.h(12)
qcE.h(qrE[6])
qcE.barrier(label='Radiation')
qcE.draw(output='mpl', fold=80, scale=0.9)
forward_qc1 = scrambler_fwd.draw_forward_circuit(fold=50)
inverse_qc1 = scrambler_fwd.draw_inverse_circuit(fold=50)
scrambler_fwd.visualize_analysis(save_path='analysis.png')
Analysis saved to: analysis.png
results = bell_swap_tests(qcE, qrE)
# Mapping bit strings to Bell states
bell_states = {'00': '|Φ+⟩', '01': '|Ψ+⟩', '10': '|Φ-⟩', '11': '|Ψ-⟩'}
for key, name in [('original', 'Original Bell (A ↔ R) - q5↔q0 [LOSS]'),
('cross', 'Cross-side (A ↔ R\') - q5↔q8 [RECOVERY]')]:
bell_counts = results[key]
total = sum(bell_counts.values())
print(f"\n{name}:")
for bs, bell_name in bell_states.items():
prob = bell_counts[bs] / total
# '00' corresponds to |Φ+⟩ - maximally entangled Bell state
success = ' ✓' if bs == '00' else ''
print(f" {bell_name}: {bell_counts[bs]:4d} ({prob:.4f}) {bar}{success}")
# P_EPR is probability of measuring |Φ+⟩ state
# Theoretical threshold for successful recovery: P_EPR ≥ 0.25
p_epr = bell_counts['00'] / total
status = "SUCCESS" if p_epr >= 0.25 else "FAILED"
print(f"P_EPR = {p_epr:.4f} [{status}]")
print("Swap Test (q0 ↔ q8):")
fidelity = results['swap']['fidelity']
swap_counts = results['swap']['counts']
p_0 = swap_counts.get('0', 0) / 8192
p_1 = swap_counts.get('1', 0) / 8192
print(f" |0⟩: {swap_counts.get('0', 0):4d} ({p_0:.4f})")
print(f" |1⟩: {swap_counts.get('1', 0):4d} ({p_1:.4f})")
print(f"\nFidelity = {fidelity:.4f}")
print(f"Status: {'BETTER ENTANGLEMENT' if fidelity > 0.8 else 'WORST ENTANGLEMENT'}")
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
gs = fig.add_gridspec(1, 3, width_ratios=[1, 1, 1])
# Plots for Bell measurements
for idx, (key, name) in enumerate([('original', 'Original Bell (A ↔ R)\nq5↔q0 [LOSS]'),
('cross', 'Cross-side (A ↔ R\')\nq5↔q8 [RECOVERY]')]):
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[idx])
bell_counts = results[key]
total = sum(bell_counts.values())
labels = list(bell_states.values())
values = [bell_counts[bs]/total for bs in ['00', '01', '10', '11']]
# Green for |Φ+⟩ (success), gray for others
colors = ['#95bb9a' if bs == '00' else '#bbb9bc' for bs in ['00', '01', '10', '11']]
ax.bar(labels, values, color=colors, edgecolor='black', linewidth=2)
# Red line at 0.25 = theoretical threshold for success
ax.axhline(y=0.25, color='red', linestyle='--', label='Threshold 0.25')
ax.set_ylabel('Probability')
ax.set_title(name)
ax.legend()
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
# Plot for Swap test
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[2])
swap_counts = results['swap']['counts']
labels = ['|0⟩', '|1⟩']
values = [swap_counts.get('0', 0)/8192, swap_counts.get('1', 0)/8192]
colors = ['#95bb9a', '#bbb9bc']
ax.bar(labels, values, color=colors, edgecolor='black', linewidth=2)
ax.set_ylabel('Probability')
ax.set_title(f'Swap Test q0↔q8\nFidelity = {fidelity:.4f}')
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Original Bell (A ↔ R) - q5↔q0 [LOSS]: |Φ+⟩: 1992 (0.2432) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) ✓ |Ψ+⟩: 2140 (0.2612) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) |Φ-⟩: 2021 (0.2467) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) |Ψ-⟩: 2039 (0.2489) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) P_EPR = 0.2432 [FAILED] Cross-side (A ↔ R') - q5↔q8 [RECOVERY]: |Φ+⟩: 2052 (0.2505) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) ✓ |Ψ+⟩: 2057 (0.2511) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) |Φ-⟩: 2078 (0.2537) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) |Ψ-⟩: 2005 (0.2448) Rectangle(xy=(2.6, 0), width=0.8, height=3.97882, angle=0) P_EPR = 0.2505 [SUCCESS] Swap Test (q0 ↔ q8): |0⟩: 6245 (0.7623) |1⟩: 1947 (0.2377) Fidelity = 0.5247 Status: WORST ENTANGLEMENT
from IPython.display import Image
Image(url='https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bluemoondom/quantum/refs/heads/quantum/yoshida2018.jpg')
References and Further Study¶
Key Papers:¶
- Hayden, Preskill (2007): "Black holes as mirrors: quantum information in random subsystems" Link: arXiv:0708.4025
- Yoshida, Kitaev (2017): "Efficient decoding for the Hayden-Preskill protocol" Link: arXiv:1806.02807 Link: Yoshida presentation
- Sekino, Susskind (2008): "Fast scramblers" Link: arXiv:0808.2096
- MuSeong Kim (2022): "Scrambling and Quantum Teleportation" Link: arXiv:2211.10068
import numpy as np
from qiskit import QuantumCircuit
from qiskit.quantum_info import Operator
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle
class ScramblingCircuit:
def __init__(self, n_qubits=5, n_layers=3, seed=None, qubit_offset=0):
"""
Args:
n_qubits: number of qubits for scrambling
n_layers: number of scrambling layers
seed: seed for reproducibility
qubit_offset: starting qubit index (default 0)
"""
self.n_qubits = n_qubits
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.qubit_offset = qubit_offset
self.rng = np.random.RandomState(seed)
# Store rotation parameters for each layer
self.rotation_params = []
def generate_scrambling_circuit(self, total_qubits=None):
"""
Generate forward scrambling circuit
Args:
total_qubits: total number of qubits in circuit (None = n_qubits + offset)
"""
if total_qubits is None:
total_qubits = self.n_qubits + self.qubit_offset
qc = QuantumCircuit(total_qubits)
self.rotation_params = [] # Reset parameters
for layer in range(self.n_layers):
layer_params = {}
# 1. RXX(π/2) gates between adjacent qubits (with offset)
for i in range(self.n_qubits - 1):
q1 = i + self.qubit_offset
q2 = i + 1 + self.qubit_offset
qc.rxx(np.pi/2, q1, q2)
# 2. Random single-qubit rotations RY and RZ (with offset)
ry_angles = self.rng.uniform(0, 2*np.pi, self.n_qubits)
rz_angles = self.rng.uniform(0, 2*np.pi, self.n_qubits)
for i in range(self.n_qubits):
q = i + self.qubit_offset
qc.ry(ry_angles[i], q)
qc.rz(rz_angles[i], q)
# Store parameters for this layer
layer_params['ry'] = ry_angles.copy()
layer_params['rz'] = rz_angles.copy()
self.rotation_params.append(layer_params)
# 3. RXX gates with shifted pattern (with offset)
for i in range(0, self.n_qubits - 1, 2):
if i + 1 < self.n_qubits:
q1 = i + self.qubit_offset
q2 = i + 1 + self.qubit_offset
qc.rxx(np.pi/2, q1, q2)
# Barrier for clarity (only on scrambling qubits)
qc.barrier(range(self.qubit_offset, self.qubit_offset + self.n_qubits))
return qc
def generate_inverse_circuit(self, total_qubits=None):
"""
Generate inverse circuit for unscrambling
Args:
total_qubits: total number of qubits in circuit (None = n_qubits + offset)
"""
if not self.rotation_params:
raise ValueError("You must generate forward circuit first!")
if total_qubits is None:
total_qubits = self.n_qubits + self.qubit_offset
qc = QuantumCircuit(total_qubits)
# Apply layers in reverse order
for layer in reversed(range(self.n_layers)):
params = self.rotation_params[layer]
# Inverse RXX gates (with shifted pattern and offset)
for i in range(0, self.n_qubits - 1, 2):
if i + 1 < self.n_qubits:
q1 = i + self.qubit_offset
q2 = i + 1 + self.qubit_offset
qc.rxx(-np.pi/2, q1, q2)
# Inverse single-qubit rotations (opposite angle and order, with offset)
for i in range(self.n_qubits):
q = i + self.qubit_offset
qc.rz(-params['rz'][i], q)
qc.ry(-params['ry'][i], q)
# Inverse RXX between neighbors (with offset)
for i in reversed(range(self.n_qubits - 1)):
q1 = i + self.qubit_offset
q2 = i + 1 + self.qubit_offset
qc.rxx(-np.pi/2, q1, q2)
# Barrier (only on scrambling qubits)
qc.barrier(range(self.qubit_offset, self.qubit_offset + self.n_qubits))
return qc
def get_parameters(self):
"""Return stored parameters"""
return self.rotation_params
def set_parameters(self, params):
"""Set parameters from previous run"""
self.rotation_params = params
def draw_forward_circuit(self, style='iqp', fold=None, save_path=None, total_qubits=None):
"""
Visualize forward circuit only
Args:
style: drawing style ('iqp', 'clifford', 'bw', 'textbook')
fold: fold at how many columns (None = no folding)
save_path: path to save (None = display only)
total_qubits: total number of qubits (None = auto)
"""
forward_circuit = self.generate_scrambling_circuit(total_qubits)
actual_qubits = total_qubits if total_qubits else (self.n_qubits + self.qubit_offset)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(18, actual_qubits * 0.8))
forward_circuit.draw('mpl', ax=ax, style=style, fold=fold)
ax.set_title(f'Forward Scrambling Circuit ({self.n_qubits} qubits, offset={self.qubit_offset}, {self.n_layers} layers)',
fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.tight_layout()
if save_path:
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
print(f"Forward circuit saved to: {save_path}")
plt.show()
return forward_circuit
def draw_inverse_circuit(self, style='iqp', fold=None, save_path=None, total_qubits=None):
"""
Visualize inverse circuit only
Args:
style: drawing style ('iqp', 'clifford', 'bw', 'textbook')
fold: fold at how many columns (None = no folding)
save_path: path to save (None = display only)
total_qubits: total number of qubits (None = auto)
"""
if not self.rotation_params:
# If parameters haven't been generated yet, generate forward first
_ = self.generate_scrambling_circuit(total_qubits)
inverse_circuit = self.generate_inverse_circuit(total_qubits)
actual_qubits = total_qubits if total_qubits else (self.n_qubits + self.qubit_offset)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(18, actual_qubits * 0.8))
inverse_circuit.draw('mpl', ax=ax, style=style, fold=fold)
ax.set_title(f'Inverse (Unscrambling) Circuit ({self.n_qubits} qubits, offset={self.qubit_offset}, {self.n_layers} layers)',
fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.tight_layout()
if save_path:
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
print(f"Inverse circuit saved to: {save_path}")
plt.show()
return inverse_circuit
def visualize_analysis(self, save_path=None):
"""
Complete visualization with 5 plots (WITHOUT circuit diagrams)
- Rotation parameters heatmap
- Forward unitary matrix
- Inverse unitary matrix
- Combined (Forward × Inverse) matrix
- Fidelity test + Circuit statistics
"""
# First generate both circuits
forward_circuit = self.generate_scrambling_circuit()
inverse_circuit = self.generate_inverse_circuit()
# Create figure with plots
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(18, 10))
gs = fig.add_gridspec(2, 3, hspace=0.3, wspace=0.3)
# 1. Rotation parameters visualization
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 0])
self._plot_rotation_parameters(ax1)
# 2. Unitary matrix - Forward
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1])
U_forward = Operator(forward_circuit).data
self._plot_unitary_matrix(ax2, U_forward, 'Forward Unitary Matrix')
# 3. Unitary matrix - Inverse
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 2])
U_inverse = Operator(inverse_circuit).data
self._plot_unitary_matrix(ax3, U_inverse, 'Inverse Unitary Matrix')
# 4. Invertibility test - complete circuit
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 0])
test_circuit = QuantumCircuit(self.n_qubits + self.qubit_offset)
test_circuit.compose(forward_circuit, inplace=True)
test_circuit.compose(inverse_circuit, inplace=True)
U_test = Operator(test_circuit).data
self._plot_unitary_matrix(ax4, U_test, 'Forward × Inverse\n(should be Identity)')
# 5. Fidelity with identity
ax5 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 1])
self._plot_fidelity_test(ax5)
# 6. Circuit statistics
ax6 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 2])
self._plot_circuit_statistics(ax6, forward_circuit, inverse_circuit)
plt.suptitle(f'Scrambling Analysis\n({self.n_qubits} qubits, offset={self.qubit_offset}, {self.n_layers} layers)',
fontsize=16, fontweight='bold', y=0.98)
if save_path:
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
print(f"Analysis saved to: {save_path}")
plt.show()
def _plot_rotation_parameters(self, ax):
"""Visualize stored rotation parameters"""
n_params = len(self.rotation_params)
# Prepare data
ry_data = np.array([layer['ry'] for layer in self.rotation_params])
rz_data = np.array([layer['rz'] for layer in self.rotation_params])
# Create heatmap
combined_data = np.vstack([ry_data, rz_data])
im = ax.imshow(combined_data, cmap='twilight', aspect='auto',
vmin=0, vmax=2*np.pi)
# Set axes
ax.set_yticks(range(2 * n_params))
labels = []
for i in range(n_params):
labels.append(f'L{i}-RY')
labels.append(f'L{i}-RZ')
ax.set_yticklabels(labels, fontsize=9)
ax.set_xlabel(f'Qubit (offset={self.qubit_offset})', fontsize=10)
ax.set_title('Rotation Parameters (radians)', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
# Colorbar
cbar = plt.colorbar(im, ax=ax, fraction=0.046, pad=0.04)
cbar.set_label('Angle (rad)', fontsize=9)
# Add values to cells (only for smaller number of qubits)
if self.n_qubits <= 8:
for i in range(combined_data.shape[0]):
for j in range(combined_data.shape[1]):
text = ax.text(j, i, f'{combined_data[i, j]:.2f}',
ha="center", va="center", color="white",
fontsize=7, fontweight='bold')
def _plot_unitary_matrix(self, ax, U, title):
"""Visualize unitary matrix (amplitude)"""
U_abs = np.abs(U)
im = ax.imshow(U_abs, cmap='viridis', aspect='equal')
ax.set_title(title, fontsize=11, fontweight='bold')
ax.set_xlabel('Column', fontsize=9)
ax.set_ylabel('Row', fontsize=9)
# Colorbar
cbar = plt.colorbar(im, ax=ax, fraction=0.046, pad=0.04)
cbar.set_label('|Amplitude|', fontsize=8)
def _plot_fidelity_test(self, ax):
"""Fidelity test with identity"""
# Create test circuit
forward_circuit = self.generate_scrambling_circuit()
inverse_circuit = self.generate_inverse_circuit()
test_circuit = QuantumCircuit(self.n_qubits + self.qubit_offset)
test_circuit.compose(forward_circuit, inplace=True)
test_circuit.compose(inverse_circuit, inplace=True)
U_test = Operator(test_circuit).data
U_identity = np.eye(2**(self.n_qubits + self.qubit_offset))
# Calculate fidelity
fidelity = np.abs(np.trace(U_test @ U_identity.conj().T)) / 2**(self.n_qubits + self.qubit_offset)
# Visualize as gauge
ax.barh([0], [fidelity], color='green' if fidelity > 0.999 else 'orange', height=0.3)
ax.set_xlim([0, 1])
ax.set_ylim([-0.5, 0.5])
ax.set_xlabel('Fidelity', fontsize=10)
ax.set_title(f'Invertibility Test\nFidelity = {fidelity:.10f}',
fontsize=11, fontweight='bold')
ax.set_yticks([])
# Add reference lines
ax.axvline(x=0.999, color='red', linestyle='--', linewidth=2, alpha=0.5,
label='Target (0.999)')
ax.axvline(x=1.0, color='blue', linestyle='--', linewidth=2, alpha=0.5,
label='Perfect (1.0)')
ax.legend(fontsize=8, loc='upper left')
# Text annotation
status = "PASSED" if fidelity > 0.999 else "FAILED"
color = 'green' if fidelity > 0.999 else 'red'
ax.text(0.5, 0, status, ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=20, fontweight='bold', color=color)
def _plot_circuit_statistics(self, ax, forward_circuit, inverse_circuit):
"""Circuit statistics"""
ax.axis('off')
stats = [
("Number of qubits:", self.n_qubits),
("Qubit offset:", self.qubit_offset),
("Number of layers:", self.n_layers),
("", ""),
("Forward circuit:", ""),
(" Depth:", forward_circuit.depth()),
(" Gate count:", forward_circuit.size()),
(" RXX gates:", forward_circuit.count_ops().get('rxx', 0)),
(" RY gates:", forward_circuit.count_ops().get('ry', 0)),
(" RZ gates:", forward_circuit.count_ops().get('rz', 0)),
("", ""),
("Inverse circuit:", ""),
(" Depth:", inverse_circuit.depth()),
(" Gate count:", inverse_circuit.size()),
(" RXX gates:", inverse_circuit.count_ops().get('rxx', 0)),
(" RY gates:", inverse_circuit.count_ops().get('ry', 0)),
(" RZ gates:", inverse_circuit.count_ops().get('rz', 0)),
]
y_pos = 0.95
for label, value in stats:
if label == "":
y_pos -= 0.05
else:
fontweight = 'bold' if ':' not in label or label.endswith(':') else 'normal'
ax.text(0.1, y_pos, f"{label} {value}",
fontsize=10, fontweight=fontweight,
transform=ax.transAxes, family='monospace')
y_pos -= 0.05
ax.set_title('Circuit Statistics', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')